| Product name | phorate |
|---|
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | Geomet |
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Insecticide |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 2
Acute toxicity - Dermal, Category 1
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, short-term (Acute) - Category Acute 1
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term (Chronic) - Category Chronic 1
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements| Pictogram(s) |   |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statement(s) | H300 Fatal if swallowed H310 Fatal in contact with skin H410 Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P262 Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P273 Avoid release to the environment. |
| Response | P301+P310 IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P321 Specific treatment (see ... on this label). P330 Rinse mouth. P302+P352 IF ON SKIN: Wash with plenty of water/... P310 Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P361+P364 Take off immediately all contaminated clothing and wash it before reuse. P391 Collect spillage. |
| Storage | P405 Store locked up. |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
none
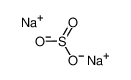
3.Composition/information on ingredients 3.1 Substances| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| phorate | phorate | 298-02-2 | none | 100% |
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaledFresh air, rest. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contactRemove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. Refer for medical attention .
In case of eye contactFirst rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowedRinse mouth. Give one or two glasses of water to drink. Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayedThis material is one of the more toxic organophosphorus insecticides. It is a cholinesterase inhibitor that acts on the nervous system, and produces toxicity similar to Parathion. The probable oral lethal dose for humans is less than 5 mg/kg, i.e. a taste (less than 7 drops) for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person. (EPA, 1998)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessaryAirway protection. Ensure that a clear airway exists. Intubate the patients and aspirate the secretions with a large-bore suction device if necessary. Administer oxygen by mechanically assisted pulmonary ventilation if respiration is depressed. Improve tissue oxygenation as much as possible before administering atropine, so as to minimize the risk of ventricular fibrillation. In severe poisonings, it may be necessary to support pulmonary ventilation mechanically for several days. /Organophosphate pesticides/
5.Fire-fighting measures 5.1 Extinguishing media Suitable extinguishing mediaIf material on fire or involved in fire: Do not extinguish fire unless flow can be stopped. Use water in flooding quantities as fog. Solid streams of water may be ineffective. Cool all affected containers with flooding quantities of water. Apply water from as far a distance as possible. Use "alcohol" foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide. /Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, flammable, toxic; Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic/
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemicalShock can shatter containers, releasing the contents. When heated to decomposition, toxic fumes of sulfur oxides, phosphorus oxides, and nitrogen oxides are emitted. Hydrolyzed in water and alkalies. (EPA, 1998)
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fightersWear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures 6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency proceduresUse personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautionsCollect leaking and spilled liquid in sealable containers as far as possible. Absorb remaining liquid in sand or inert absorbent. Then store and dispose of according to local regulations. Do NOT let this chemical enter the environment. Personal protection: gas-tight chemical protection suit including self-contained breathing apparatus.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning upEnvironmental considerations: Air spill: Apply water spray or mist to knock down vapors. /Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, flammable, toxic; Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic; Organophosphorus pesticides, solid, toxic/
7.Handling and storage 7.1 Precautions for safe handlingAvoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilitiesProvision to contain effluent from fire extinguishing. Separated from food and feedstuffs. Keep in a well-ventilated room. Store in an area without drain or sewer access. Provision to contain effluent from fire extinguishing.Provision to contain effluent from fire extinguishing. Separated from food and feedstuffs. Keep in a well-ventilated room.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection 8.1 Control parameters Occupational Exposure limit valuesRecommended Exposure Limit: 10 Hr Time-Weighted Avg: 0.05 mg/cu m.
Recommended Exposure Limit: 15 Min Short-Term Exposure Limit: 0.2 mg/cu m, skin.
Biological limit valuesno data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controlsHandle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE) Eye/face protectionSafety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protectionWear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protectionWear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazardsno data available
9.Physical and chemical properties| Physical state | liquid |
|---|---|
| Colour | Pale straw to light brown; colorless to very light yellow liquid. |
| Odour | Skunk-like odor |
| Melting point/ freezing point | -43ºC |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 125-127ºC (2 mmHg) |
| Flammability | Class IIIB Combustible Liquid: Fl.P. at or above 93.33°C., but does not readily ignite.Combustible. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | no data available |
| Flash point | 132.8ºC |
| Auto-ignition temperature | no data available |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | no data available |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | In water:0.005 g/100 mL |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | log Kow = 3.56 |
| Vapour pressure | 0.0026mmHg at 25°C |
| Density and/or relative density | 1.201g/cm3 |
| Relative vapour density | no data available |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
no data available
10.2 Chemical stabilityStable at room temp.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactionsOrganothiophosphates, such as PHORATE, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
10.4 Conditions to avoidno data available
10.5 Incompatible materialsIncompatible with alkaline compounds and with water-containing preparations.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition productsWhen heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /phosphorous and sulfur oxides/.
11.Toxicological information Acute toxicity- Oral: LD50 Rat male oral 2 mg/kg
- Inhalation: LC50 Rat (male) inhalation 0.06 mg/cu L/1 hr /Analytical grade phorate aerosol/
- Dermal: LD50 Rabbit percutaneous male 93-245 mg active ingredient (as 5% granule)/kg, acute
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritationno data available
Respiratory or skin sensitizationno data available
Germ cell mutagenicityno data available
CarcinogenicityCancer Classification: Group E Evidence of Non-carcinogenicity for Humans
Reproductive toxicityno data available
STOT-single exposureno data available
STOT-repeated exposureno data available
Aspiration hazardno data available
12.Ecological information 12.1 Toxicity- Toxicity to fish: LC50 Salmo gairdneri (Rainbow trout) 13 ug/l/96 hr @ 12°C (95% confidence limit 11-16 ug/l), wt 1.2 g. Static bioassay without aeration, pH 7.2-7.5, water hardness 40-50 mg/l as calcium carbonate and alkalinity of 30-35 mg/l. /Technical, 100%
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: no data available
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
Degradation half-lives of phorate in various soils were: sandy loam, 7 days; silty clay loam, 9 days; and clay loam, 8 days(1). One-half of the applied phorate dosage to silt loam soil could no longer be detected after 6 days when applied to the soil surface and after 30 days when mixed with the upper 4-5 inch soil layer(2). In silt loam soil, phorate persisted beyond 16 weeks at 25°C(3). The half-life of phorate in clay loam soil when applied as a granular formulation ranged from 5 to 10 days(4). In a field study, 67 and 70% of phorate was lost within 28 days from silty clay loam soil(5). Bioassays indicate the half-life of phorate, when applied to the top 4 inches of sandy loam soil at a concentration of 10 ppm, is about 68 days(6). In flooded agricultural loam soil, 1.7, 6.0, and 9.9% of the applied C14-phorate had been evolved as C14-CO2 after 3, 7, and 14 days incubation, respectively(7). In non-flooded soils, 1.3, 2.3, and 3.3% of the applied C14-phorate had been evolved as C14-CO2 after identical incubation periods(7). Half-lives of 1.2 days and 1.1 days were determined for phorate in active sediment and water, respectively(8). In a 1 week laboratory assay, phorate mineralization was not significantly greater in soils with a history of phorate use than in soils with no history of phorate use(9). The microbial degradation of phorate in loam soil, sandy soil, and muck soil led to the formation of phorate sulfone and phorate sulfoxide; formation was much less in sandy soil(10). Phorate, when applied at a rate of 1.25 kg AI/ha to black clay loam soils under flooded conditions, degraded quickly(11). In shake flask tests, phorate showed more degradation in the presence of non-sterile estuarine sediment, half-life of about 1 day, than in the presence of sterile sediment, half-life of about 1.5 days(12). The half-lives of phorate in shake flasks containing a non-sterile sediment-water slurry were less than 1 day(12). In studies where 32 farm soils were incubated with phorate, initial half-lives of freshly-applied phorate ranged from <1 to >16 weeks(13). Accelerated degradation was stimulated by a single application and occurred most readily at pH's >7.4(13).
12.3 Bioaccumulative potentialJuvenile sheepshead minnows, Cyprinodon variegatus, after 28 days exposure to phorate had a BCF of 90(1). According to a classification scheme(2), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is moderate(SRC). Bioconcentration of phorate from culture media by the blue green algae Anabaena sp. (ARM 310) and Aulosira fertilissima (ARM 68) was studied(1). Bioconcentration factors for phorate in Anabaena sp. were 3, 6 and 12 at 2.5, 5 and 10 ug/ml, respectively(3). In Anabaena fertilissima, at 2.5, 5 and 10 ug/ml of phorate, max bioconcentration of phorate was reached after 16, 16 and 32 hr, respectively, with bioconcentration factors of 8, 12 and 11 for the respective doses(3). Elodea nuttallii plants grown for 2 weeks in water with a deposit of C14-phorate in the bottom soil accumulated 30% of the originally soil-applied radiocarbon in their tissues; 56% of phorate accumulated in plant tissues when the insecticide was applied directly to the water(4).
12.4 Mobility in soilIn four different soils with percent organic carbon ranging from 0.087 to 0.65, phorate had an average Koc of 3200(1). Koc values of 543(2) and 2400(3) have also been reported for phorate. Phorate was found to be only slightly mobile in soil column studies(4). Phorate was less mobile in degraded chernozem and in black marsh soil, than in brown forest soil(4). According to a classification scheme(5), these Koc values suggest that phorate is expected to have low to slight mobility in soil. Phorate is most readily adsorbed to mineral solids and to silty loam and clay soils when the soils are dry(4). A soil mobility factor of 1.2 was calculated for phorate using soil column studies with Hagerstown silty clay loam (4.3% organic matter, 30% clay, pH 5.5) and Lakeland sandy loam(3.3% organic matter, 10% clay, pH 6.2)(6). A mobility factor of 1 represents no movement, while a mobility factor of 6 represents maximum movement(7). In a field study using watershed soils and their corresponding pond sediments, phorate was adsorbed more extensively by pond sediments (organic matter 1.4%, clay content 25%) than by Ca-saturated soils (organic matter 2.4%, clay content 16%)(7).
12.5 Other adverse effectsno data available
13.Disposal considerations 13.1 Disposal methods ProductThe material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packagingContainers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information 14.1 UN Number| ADR/RID: UN2810 | IMDG: UN2810 | IATA: UN2810 |
| ADR/RID: TOXIC LIQUID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. |
| IMDG: TOXIC LIQUID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. |
| IATA: TOXIC LIQUID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. |
| ADR/RID: 6.1(a) | IMDG: 6.1(a) | IATA: 6.1(a) |
| ADR/RID: I | IMDG: I | IATA: I |
| ADR/RID: yes | IMDG: yes | IATA: yes |
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Codeno data available
15.Regulatory information 15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| phorate | phorate | 298-02-2 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Not Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
| Creation Date | Aug 13, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 13, 2017 |
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/