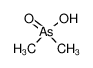
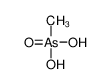
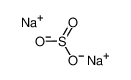
| Product name | dimethylarsinic acid |
|---|
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | Silvisar |
| Identified uses | For industry use only. |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 3
Acute toxicity - Inhalation, Category 3
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, short-term (Acute) - Category Acute 1
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term (Chronic) - Category Chronic 1
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements| Pictogram(s) |   |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statement(s) | H301 Toxic if swallowed H331 Toxic if inhaled H410 Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P261 Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271 Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273 Avoid release to the environment. |
| Response | P301+P310 IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P321 Specific treatment (see ... on this label). P330 Rinse mouth. P304+P340 IF INHALED: Remove person to fresh air and keep comfortable for breathing. P311 Call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P391 Collect spillage. |
| Storage | P405 Store locked up. P403+P233 Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients 3.1 Substances| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| dimethylarsinic acid | dimethylarsinic acid | 75-60-5 | none | 100% |
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaledIf breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
In case of skin contactWash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
In case of eye contactRinse thoroughly with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and consult a physician.
If swallowedNever give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayedChemical is essentially non-irritating in contact with skin or eyes. Ingestion causes arsenic poisoning, but symptoms are delayed. (USCG, 1999)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessaryFIRST AID: Get medical aid. Eyes, skin, flush with flowing water immediately and continuously for 15 minutes. Inhalation, materials nonvolatile but if spray drift is inhaled, treat as ingestion. ... May be treated as for general arsenic poisoning.
5.Fire-fighting measures 5.1 Extinguishing media Suitable extinguishing mediaIf material on fire or involved in fire: Extinguish fire using agent suitable for type of surrounding fire. (Material itself does not burn or burns with difficulty.) Use water in flooding quantities as fog. Use foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide. Keep run-off water out of water sources and sewers.
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemicalBehavior in Fire: May form toxic oxides of arsenic when heated. (USCG, 1999)
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fightersWear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures 6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency proceduresUse personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautionsPrevent further leakage or spillage if safe to do so. Do not let product enter drains. Discharge into the environment must be avoided.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning upPick up and arrange disposal. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed containers for disposal.
7.Handling and storage 7.1 Precautions for safe handlingAvoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilitiesKEEP WELL CLOSED.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection 8.1 Control parameters Occupational Exposure limit valuesno data available
Biological limit valuesno data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controlsHandle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE) Eye/face protectionSafety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protectionWear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protectionWear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazardsno data available
9.Physical and chemical properties| Physical state | colorless or white crystalline powder |
|---|---|
| Colour | Crystals from alcohol and ether |
| Odour | Odorless |
| Melting point/ freezing point | 195-198ºC |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 253.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Flammability | no data available |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | no data available |
| Flash point | no data available |
| Auto-ignition temperature | no data available |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | no data available |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | Very soluble |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | no data available |
| Vapour pressure | no data available |
| Density and/or relative density | >1.1(20ºC) |
| Relative vapour density | no data available |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
no data available
10.2 Chemical stabilityCOMPLETELY STABLE IN STORAGE.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactionsNonflammableCACODYLIC ACID is a weak acid. Dissolves in water to yield solutions containing more hydrogen ions than pure water contains and so having a pH less than 7.0. Is neutralized exothermically by all bases to produce water plus a salt. Reacts (but usually slowly) with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for the solid acid but are quite slow if the solid acid remains dry. The solid may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in it to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Reacts with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat may be generated with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Also may react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still some heat. Can be oxidized exothermically by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents; a wide variety of products is possible. May initiate polymerization reactions; may catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
10.4 Conditions to avoidno data available
10.5 Incompatible materialsHAZARDOUS WHEN WATER SOLN IS IN CONTACT WITH ACTIVE METALS, E.G., /IRON, ALUMINUM, AND ZINC/.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition productsWhen heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /arsenics/.
11.Toxicological information Acute toxicity- Oral: LD50 Rat oral 700 mg/kg
- Inhalation: LC50 Rat male inhalation (exposure to dust): > 6.9 mg/l/2 hr
- Dermal: no data available
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritationno data available
Respiratory or skin sensitizationno data available
Germ cell mutagenicityno data available
CarcinogenicityCancer Classification: Group B2 Probable Human Carcinogen
Reproductive toxicityno data available
STOT-single exposureno data available
STOT-repeated exposureno data available
Aspiration hazardno data available
12.Ecological information 12.1 Toxicity- Toxicity to fish: no data available
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: no data available
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
DEGRADATION OF CACODYLIC ACID TO CARBON DIOXIDE & ARSENATE /IN SOIL/ APPEARS TO BE MICROBIAL IN NATURE & IS PROBABLY DEPENDENT ON SOIL ORGANIC MATTER CONTENT ... .
12.3 Bioaccumulative potentialA BCF of 21 was measured for mosquito fish in a model ecosystem study(1). According to a classification scheme(2), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4 Mobility in soilOrganoarsenicals, such as dimethylarsinic acid, are adsorbed by clays soils(1). After rapid initial adsorption, changes occur which result in the redistribution of dimethylarsinic acid into a less soluble form associated with aluminum in the soil(1). The dimethylarsinic acid are fixed by iron and aluminum in the soil, although not as strongly as inorganic arsenate(1). Leaching tests conducted in specially constructed boxes with clay, silt loam, and sandy soils noted strong adsorption to all soils, although a small degree of leaching did occur(2). The adsorption of dimethylarsenic acid to sediments and soil was found to depend on clay content, iron oxide content, and pH(3,4); adsorption increases with increasing clay and iron oxide content and with higher pH(3,4). Herbicidal applications of dimethylarsenic acid that were applied to forest floors in the northwestern US were found to be tightly bound, and did not leach in soil(5).
12.5 Other adverse effectsno data available
13.Disposal considerations 13.1 Disposal methods ProductThe material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packagingContainers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information 14.1 UN Number| ADR/RID: UN1572 | IMDG: UN1572 | IATA: UN1572 |
| ADR/RID: CACODYLIC ACID |
| IMDG: CACODYLIC ACID |
| IATA: CACODYLIC ACID |
| ADR/RID: 6.1 | IMDG: 6.1 | IATA: 6.1 |
| ADR/RID: II | IMDG: II | IATA: II |
| ADR/RID: yes | IMDG: yes | IATA: yes |
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Codeno data available
15.Regulatory information 15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| dimethylarsinic acid | dimethylarsinic acid | 75-60-5 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Not Listed. | ||
| Creation Date | Aug 16, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 16, 2017 |
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/