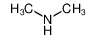
| Product name | Dimethylamine |
|---|
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | N-methylmethanamine |
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Agricultural chemicals (non-pesticidal),Intermediates,Ion exchange agents,Lubricants and lubricant additives,Paint additives and coating additives not described by other categories |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
no data available
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements| Pictogram(s) | no data available |
|---|---|
| Signal word | no data available |
| Hazard statement(s) | no data available |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | no data available |
| Response | no data available |
| Storage | no data available |
| Disposal | no data available |
no data available
3.Composition/information on ingredients 3.1 Substances| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimethylamine | Dimethylamine | 124-40-3 | none | 100% |
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaledFresh air, rest. Half-upright position. Artificial respiration may be needed. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contactON FROSTBITE: rinse with plenty of water, do NOT remove clothes. Refer for medical attention .
In case of eye contactFirst rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowedRinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. Give one or two glasses of water to drink. Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayedVAPOR: Irritating to eyes, nose and throat. If inhaled, will cause difficult breathing. LIQUID. Will burn skin and eyes. Harmful if swallowed. (USCG, 1999)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessaryBasic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if necessary. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mg/kg up to 200 ml of water for dilution if the patent can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool. Administer activated charcoal ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Organic bases/Amines and related compounds/
5.Fire-fighting measures 5.1 Extinguishing media Suitable extinguishing mediaStop flow of gas before extinguishing fire. Use water spray to keep fire-exposed containers cool. Use water spray, dry chemical, or "alcohol resistant" foam on fires involving aqueous solutions.
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemicalFLAMMABLE. Flashback along vapor trail may occur. May explode if ignited in an enclosed area. Vapors are eye, skin and respiratory irritants. (USCG, 1999)
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fightersWear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures 6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency proceduresUse personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautionsEvacuate danger area! Consult an expert! Personal protection: complete protective clothing including self-contained breathing apparatus. Ventilation. Remove all ignition sources. NEVER direct water jet on liquid. Remove gas with fine water spray. Do NOT let this chemical enter the environment.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning upEnvironmental considerations-land spill: Dig a pit, pond, lagoon, holding area to contain liquid or solid material. /SRP: If time permits, pits, ponds, lagoons, soak holes, or holding areas should be sealed with an impermeable flexible membrane liner./ Dike surface flow using soil, sand bags, foamed polyurethane, or foamed concrete. Absorb bulk liquid with fly ash, cement powder, or commercial sorbents. Apply "universal" gelling agent to immobilize spill. Neutralize with sodium bisulfate (NaHSO4). /Dimethylamine, Solution/
7.Handling and storage 7.1 Precautions for safe handlingAvoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilitiesFireproof. Cool.They are extremely flammable products that should be stored in a well-ventilated area and protected from fire risk. /Methylamines/
8.Exposure controls/personal protection 8.1 Control parameters Occupational Exposure limit valuesRecommended Exposure Limit: 10 Hr Time-Weighted Avg: 10 ppm (18 mg/cu m).
Biological limit valuesno data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controlsHandle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE) Eye/face protectionSafety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protectionWear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protectionWear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazardsno data available
9.Physical and chemical properties| Physical state | colourless compressed liquefied gas |
|---|---|
| Colour | Colorless gas ... [Note: A liquid below 44 degrees F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas]. |
| Odour | ... Ammonia or fish-like odor ... |
| Melting point/ freezing point | -93ºC |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | 7°C(lit.) |
| Flammability | Flammable GasExtremely flammable. Gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | Lower flammable limit: 2.8% by volume; Upper flammable limit: 14.4% by volume |
| Flash point | -6°C |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 400.56°C |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | AQUEOUS SOLN OF DIMETHYLAMINE ARE HIGHLY ALKALINE, LIKE AMMONIA. |
| Kinematic viscosity | 1.7 mPa.s at 15.5°C /40% Dimethylamine aqueous solution/ |
| Solubility | 24 % at 60°C (NIOSH, 2016) |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | log Kow = -0.38 |
| Vapour pressure | 16.97 psi ( 55 °C) |
| Density and/or relative density | 0.68g/mLat 20°C(lit.) |
| Relative vapour density | 1.55 (vs air) |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
no data available
10.2 Chemical stabilityStable under recommended storage conditions.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactionsLiquid solutions are flammable.The gas is heavier than air and may travel along the ground; distant ignition possible.The vapour is heavier than air and may travel along the ground; distant ignition possible.DIMETHYLAMINE is a base, neutralizing acids in exothermic reactions, and a reducing agent. It is temperature sensitive. Reacts vigorously with mercury and chlorine . Reacts violently with strong oxidizing agents and attacks copper and copper compounds [Handling Chemicals Safely, 1980 p. 123]. Reacts with hypochlorites to give N-chloroamines, some of which are explosives when isolated [Bretherick, 1979 p. 108].
10.4 Conditions to avoidno data available
10.5 Incompatible materialsDimethylamine is a medium strong base. Reacts violently with strong oxidizers; with mercury causing fire and explosion hazard. Incompatible with acids, organic anhydrides, isocyanates, vinyl acetate, acrylates, substituted allyls, alkylene oxides, epichlorohydrin, ketones, aldehydes, alcohols, glycols, phenols, cresols, caprolactum solution. Attacks aluminum, copper, lead, tin, zinc and alloys, some plastics, rubber and coatings.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition productsProducts of decomposition include carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, and toxic oxides of nitrogen as well as toxic amine vapors.
11.Toxicological information Acute toxicity- Oral: LD50 Rat oral 698 mg/kg
- Inhalation: LC50 Mouse inhalation (2 hr) 14.3 mg/L
- Dermal: no data available
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritationno data available
Respiratory or skin sensitizationno data available
Germ cell mutagenicityno data available
CarcinogenicityA4; Not classifiable as a human carcinogen.
Reproductive toxicityno data available
STOT-single exposureno data available
STOT-repeated exposureno data available
Aspiration hazardno data available
12.Ecological information 12.1 Toxicity- Toxicity to fish: LC50 Brachydanio rerio /Zebra danio/ 396 mg/L/96 hr; static, freshwater. /Dimethylamin-Hydrochlorid
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: EC50; Species: Daphnia magna (Water flea); Conditions: freshwater, static, 15°C, pH 7.2, hardness 320 mg/L CaCO3, dissolved oxygen >95%; Concentration: 46,000 ug/L for 96 hr (95% confidence interval: 40,100-52,800 ug/L); Effect: intoxication, immobilization
- Toxicity to algae: EC50; Species: Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata (Green algae); Conditions: freshwater, static; Concentration: 9000 ug/L for 96 hr; Effect: general growth /40% water solution
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
AEROBIC: 51% of the theoretical BOD was achieved for dimethylamine with an activated sludge during a 2 week incubation period(1). Dimethylamine was biodegraded 69-89% in three Saskatchewan soils during a 7 day incubation period(2). In a screening study, dimethylamine completely degraded at 10 ppm with both an activated sludge and freshwater/sediment inoculum(3); after 5 days incubation, 70 and 80% of theoretical BOD was consumed in the activated sludge and the sediment, respectively(1). Inhibition was noted at 50 ppm with the sediment inoculum and 100 ppm with the sludge inoculum(3). Another screening study that employed an activated sludge inoculum reported 100% degradation in 6 and 12 days when the concentration was 20 mg/L and 135 mg/L, respectively(4). Other screening studies give similar results and dimethylamine is confirmed to be biodegradable according to the standard test of the Japanese Ministry of Industry and Trade (MITI) that employs a mixed inoculum obtained from freshwater, soil, and sludge(5-7). In a laboratory activated sludge unit, dimethylamine was completely removed from inflows of up to 135 mg/L with retention times of 4 hr indicating that it should be readily degraded in biological treatment plants(4). When 250 ppm dimethylamine was added to a fine sand loam and sandy soil amended with sewage and nitrite-N, 50% degradation occurred in 2 days in the sand loam, while 20% degradation occurred in the sandy soil(8). N-nitrosodimethylamine was formed in the degradation(8). 50 to >90% degradation occurred in four silt loam or loam soils within 14 days(9).
12.3 Bioaccumulative potentialAn estimated BCF of 3 was calculated in fish for dimethylamine(SRC), using a log Kow of -0.38(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4 Mobility in soilThe adsorption isotherm for dimethylamine in 5 soils was linear and resulted in a mean Koc of 434.9(1). A Koc value of 508 was reported for dimethylamine in lake sediment(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this Koc data suggests that dimethylamine is expected to have moderate mobility in soil.
12.5 Other adverse effectsno data available
13.Disposal considerations 13.1 Disposal methods ProductThe material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packagingContainers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information 14.1 UN Number| ADR/RID: UN1032 | IMDG: UN1032 | IATA: UN1032 |
| ADR/RID: DIMETHYLAMINE, ANHYDROUS |
| IMDG: DIMETHYLAMINE, ANHYDROUS |
| IATA: DIMETHYLAMINE, ANHYDROUS |
| ADR/RID: 3 | IMDG: 3 | IATA: 3 |
| ADR/RID: II | IMDG: II | IATA: II |
| ADR/RID: no | IMDG: no | IATA: no |
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Codeno data available
15.Regulatory information 15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimethylamine | Dimethylamine | 124-40-3 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
| Creation Date | Aug 12, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 12, 2017 |
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/