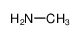| Product name | METHYLAMINE |
|---|
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | Methanamine |
| Identified uses | For industry use only. Agricultural chemicals (non-pesticidal),Intermediates,Processing aids, not otherwise listed,Processing aids, specific to petroleum production,Solvents (for cleaning or degreasing),Solvents (which become part of product formulation or mixture),Viscosity adjustors |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
| Company | MOLBASE (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Address | Floor 4 & 5, Building 12, No. 1001 North Qinzhou Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai, China |
| Telephone | +86(21)64956998 |
| Fax | +86(21)54365166 |
| Emergency phone number | +86-400-6021-666 |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
no data available
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements| Pictogram(s) | no data available |
|---|---|
| Signal word | no data available |
| Hazard statement(s) | no data available |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | no data available |
| Response | no data available |
| Storage | no data available |
| Disposal | no data available |
no data available
3.Composition/information on ingredients 3.1 Substances| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| METHYLAMINE | METHYLAMINE | 74-89-5 | none | 100% |
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaledFresh air, rest. Half-upright position. Artificial respiration may be needed. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contactON FROSTBITE: rinse with plenty of water, do NOT remove clothes. Refer for medical attention .
In case of eye contactFirst rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowedRinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. Give one or two glasses of water to drink. Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayedVAPOR: Irritating to eyes, nose and throat. If inhaled will cause coughing or difficult breathing. LIQUID: Will burn skin and eyes. (USCG, 1999)
INHALATION: Causes irritation of nose and throat, followed by violent sneezing, burning sensation in throat, coughing and difficulty in breathing, pulmonary congestion, edema of the lungs and conjunctivitis. Bronchitis occurred in a worker exposed to a workroom concentration range of 2-60 ppm. EYES: Liquid contact causes burning (severe exposure may cause blindness). SKIN: Causes burning. Vapors may cause dermatitis. INGESTION: Causes burns of the mouth, throat and esophagus. (USCG, 1999)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessaryBasic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if necessary. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% /normal/ saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mg/kg up to 200 ml of water for dilution if the patent can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool. Administer activated charcoal ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Organic bases/Amines and related compounds/
5.Fire-fighting measures 5.1 Extinguishing media Suitable extinguishing mediaMethylamine is a flammable liquid or gas. If gas, stop the flow of gas if it can be done safely. Use water to keep fire-exposed containers cool and to protect people attempting shut-off. For water solutions, use water spray, CO2, dry chemical, and alcohol foam extinguishers. Poisonous gases are produced in fire, including oxides of nitrogen. Vapors are heavier than air and will collect in low areas. Vapors may travel long distances to ignition sources and flashback. Vapors in confined areas may explode when exposed to fire. Containers may explode in fire. Storage containers and parts of containers may rocket great distances, in many directions. If material or contaminated runoff enters waterways, notify downstream users of potentially contaminated waters. Notify local health and fire officials and pollution control agencies. Containers may explode in fire. From a secure, explosion-proof location, use water spray to cool exposed containers. If cooling streams are ineffective (venting sound increases in volume and pitch, tank discolors, or shows any signs of deforming), withdraw immediately to a secure position. If employees are expected to fight fires, they must be trained and equipped in OSHA 1910.156.
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemicalFLAMMABLE. POISONOUS GASES MAY BE PRODUCED IN FIRE. Containers may explode in fire. Flashback along vapor trail may occur. Vapor may explode if ignited in an enclosed area. Toxic nitrogen oxides may be formed. Vapors are heavier than air and may travel considerable distance to a source of ignition and flash back. (USCG, 1999)
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic nitrogen oxides may be formed. Behavior in Fire: Vapors are heavier than air and may travel a considerable distance to a source of ignition and flashback. When heated to decomposition, it emits toxic fumes of NO X (USCG, 1999)
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fightersWear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures 6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency proceduresUse personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautionsEvacuate danger area! Consult an expert! Personal protection: complete protective clothing including self-contained breathing apparatus. Ventilation. Remove all ignition sources. NEVER direct water jet on liquid. Remove vapour with fine water spray.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning upLiquid: Evacuate and restrict persons not wearing protective equipment from area of spill or leak until clean-up is complete. Remove all ignition sources. Especially forced ventilation to keep levels below explosive limit. Absorb liquids in vermiculite, dry sand, earth, peat, carbon, or similar material and deposit in sealed containers. Alternatively, spread heavily with sodium bisulfate and sprinkle with water. Then drain into a sewer with a large amount of water /if the sewer is designed to prevent the build up of explosive concentrations/. Keep this chemical out of a confined space, such as a sewer, because of the possibility of an explosion, unless the sewer is designed to prevent the build up of explosive concentrations. It may be necessary to contain and dispose of this chemical as a hazardous waste. If material or contaminated runoff enters waterways, notify downstream users of potentially contaminated waters. Contact your Department of Environmental Protection or your regional office of the federal EPA for specific recommendations. If employees are required to clean-up spills, they must be properly trained and equipped. OSHA 1910.120(q) may be applicable. Gas: If in a building, evacuate building and confine vapors by closing doors and shutting down HVAC systems. Restrict persons not wearing protective equipment for area of spill or leak until cleanup is complete. Remove all ignition sources. Establish forced ventilation to keep levels below explosive limit and to disperse the gas. Wear chemical protective suit with self-contained breathing apparatus to combat spills. Stay upwind and use water spray to "knock down" vapor; contain runoff. Stop the flow of gas, if it can be done safely from a distance. If source is a cylinder and the leak cannot be stopped in place, remove the leaking cylinder to a safe place, and repair leak or allow cylinder to empty. Keep this chemical out of confined spaces, such as a sewer, because of the possibility of an explosion, unless the sewer is designed to prevent the build up of explosive concentrations. If employees are required to clean-up spills, they must be properly trained and equipped. OSHA 1910.120(q) may be applicable.
7.Handling and storage 7.1 Precautions for safe handlingAvoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilitiesFireproof. Cool.They are extremely flammable products that should be stored in a well-ventilated area and protected from fire risk. /Methylamines/
8.Exposure controls/personal protection 8.1 Control parameters Occupational Exposure limit valuesRecommended Exposure Limit: 10 Hr Time-Weighted avg: 10 ppm (12 mg/cu m).
Biological limit valuesno data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controlsHandle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE) Eye/face protectionSafety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protectionWear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protectionWear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazardsno data available
9.Physical and chemical properties| Physical state | clear liquid |
|---|---|
| Colour | Colorless gas [Note: A liquid below 21 degrees F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas]. |
| Odour | Fish or ammonia-like odor |
| Melting point/ freezing point | -93ºC |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | -6.3°C(lit.) |
| Flammability | Flammable GasExtremely flammable. Gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | 4.9-20.7% |
| Flash point | <-34°C |
| Auto-ignition temperature | 430°C |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | Stronger base than ammonia |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | greater than or equal to 100 mg/mL at 21.11°C |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | no data available |
| Vapour pressure | 27 psi ( 20 °C) |
| Density and/or relative density | 0.861g/mLat 25°C |
| Relative vapour density | 1.08 (20 °C, vs air) |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
no data available
10.2 Chemical stabilityStable under recommended storage conditions.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactionsFLAMMABLE GAS AT ORDINARY TEMP AND PRESSURE.The gas mixes well with air, explosive mixtures are easily formed.The vapour mixes well with air, explosive mixtures are easily formed.METHYLAMINE neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
10.4 Conditions to avoidno data available
10.5 Incompatible materialsA medium strong base. Reacts violently with strong acids, mercury, strong oxidizers, nitromethane. Corrosive to copper, zinc alloys, aluminum, and galvanized surfaces.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition productsWhen heated to decomp it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
11.Toxicological information Acute toxicity- Oral: LD50 Rat oral 80 mg/kg (female adults).
- Inhalation: LC50 Rat inhalation 2.9 mg/L/4 hr
- Dermal: no data available
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritationno data available
Respiratory or skin sensitizationno data available
Germ cell mutagenicityno data available
Carcinogenicityno data available
Reproductive toxicityno data available
STOT-single exposureno data available
STOT-repeated exposureno data available
Aspiration hazardno data available
12.Ecological information 12.1 Toxicity- Toxicity to fish: LC50; Species: Oncorhynchus mykiss (Rainbow trout); Conditions: freshwater, renewal, 14.5.-15.5°C, pH 7.8-9.5, dissolved oxygen 8.2-10.6 mg/L; Concentration: 56000 ug/L for 48 hr
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: no data available
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
Biological oxygen demand (BOD): 67.8% of theoretical in 13 days
12.3 Bioaccumulative potentialAn estimated BCF of 3 was calculated in fish for methylamine(SRC), using a log Kow of -0.57(1) and a regression-derived equation(2). According to a classification scheme(3), this BCF suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low(SRC).
12.4 Mobility in soilNo detectable sorption of methylamine was observed on a Podzol soil (4.85% organic C)(1). A Koc value of 389 was observed on Alfisol agricultural soil (1.25% organic C)(1). A Koc value of 449 was observed on a subliminic soil, a sediment of Lake Constance (1.58% organic C)(1). According to a classification scheme(2), these Koc values suggest that methylamine is expected to have moderate mobility in soil. Adsorption (desorption) partition coefficients for methylamine on montmorillonite and sediment were 7.0 (9.3) mL/g and 3.5 (5.4) mLg, respectively; at high concns, approx 20% of the methylamine absorbed onto montmorillonite was not desorbed(3). An adsorption partition coefficient of <1 was observed on kaolinite(3).
12.5 Other adverse effectsno data available
13.Disposal considerations 13.1 Disposal methods ProductThe material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packagingContainers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information 14.1 UN Number| ADR/RID: UN2924 | IMDG: UN2924 | IATA: UN2924 |
| ADR/RID: FLAMMABLE LIQUID, CORROSIVE, N.O.S. |
| IMDG: FLAMMABLE LIQUID, CORROSIVE, N.O.S. |
| IATA: FLAMMABLE LIQUID, CORROSIVE, N.O.S. |
| ADR/RID: 8 | IMDG: 8 | IATA: 8 |
| ADR/RID: II | IMDG: II | IATA: II |
| ADR/RID: no | IMDG: no | IATA: no |
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Codeno data available
15.Regulatory information 15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| METHYLAMINE | METHYLAMINE | 74-89-5 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
| Creation Date | Aug 16, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 16, 2017 |
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/